Thermodynamics is a branch of physics
that deals with the energy and work of a system.
Thermodynamics deals only with the
large scale response
of a system that we can observe
and measure in experiments. In aerodynamics, we are most
interested in the thermodynamics of propulsion
systems
and
high speed flows.
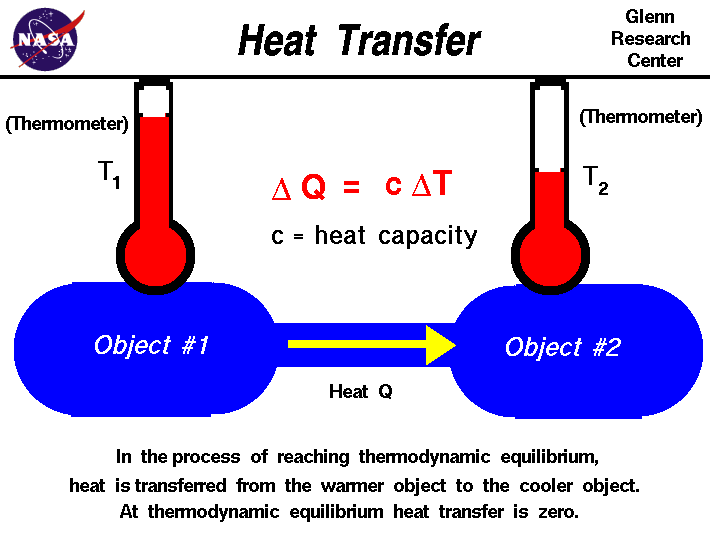
The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
introduces the concept of thermodynamic equilibrium, in which
two objects have the same temperature. If
we bring two objects that are initially at different temperatures
into physical contact, they eventually achieve thermal
equilibrium. During the process of reaching thermal equilibrium, heat
is transferred between the objects.
The amount of heat transferred delta Q is
proportional to the temperature difference delta T
between the objects and
the heat capacity c of the object.
delta Q = c * delta T
The
heat capacity
is a constant that tells how much heat is added per unit temperature rise.
The value of the constant is different for different materials. Heat
is always transferred from the object at the higher
temperature to the object
with the lower temperature.
For a gas, the heat transfer is related to a change in temperature. The
temperature,
pressure, and
volume
of the gas determine the state
of the gas. Heating a gas changes the state of the gas. But the state
of a gas can be changed in a wide variety of ways. On another slide,
we show how work done on a gas also changes
the state of the gas. The amount of work that a gas can do depends on
both the initial and final states and on the process used to make the
change. In the same way, the amount of heat transferred in changing
the state of a gas also depends on the initial and final states and
the exact process used to change the state. Different processes
result in different amounts of heat transfer and work. The effects of
both heat flow and work are combined in the First
Law of Thermodynamics.
There are some thermodynamic processes in which there is no heat transfer.
Engineers call this type of a process an adiabatic process
and there are simple
equations
which relate the pressure and temperature of a gas for an
adiabatic process.
Activities:
Guided Tours
-
 Thermodynamics:
Thermodynamics:

-
 Combustion:
Combustion:

-
 Burner:
Burner:

Navigation ..


- Beginner's Guide Home Page
|
