

Wing
Area Problems
If so instructed by your teacher, print out a worksheet page for these problems.
If so instructed by your teacher, print out a worksheet page for these problems.
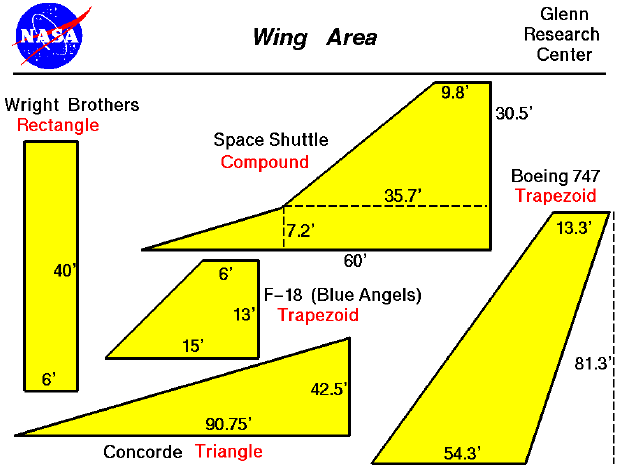
- Using the picture
and dimensions provided, calculate the area of the Wright Brothers wing
section and the F-18 Blue Angels wing. Record your answers in the data
table.
- Open the FoilSim
program. Set your airspeed =100, altitude =2,500, angle=5.0, thickness
=12.5, and camber=0. Change the area by plugging in the values you calculated
for each wing area and record the resulting lift force in your data
table.
- Graph your results
with the calculated values for area on the x-axis and the lift force
on the y-axis. (Be sure to label your graph.)
- What is the relationship
suggested by this graph?
- Find and record
the slope of your graph.
- Using the calculated
slope, write the equation for the line (on your graph) using the form
L = Constant * A, where L is the lift, constant is the slope, and A is the area. - Using your equation,
calculate the lift produced by the Boeing 747 and Concorde (area
given in table). Record your answers in the table.
- Using your equation,
calculate the area of the Space Shuttle compound wing (lift given
in table). Record your answer in the table.
- Design a trapezoid wing that will generate a lift force of 121,000 lbs. Your wing span (distance from wing tip to wing tip) may not exceed 95 feet.
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
Wright Brothers rectangle |
_______________________ |
_________________ |
|
F-18 (Blue Angels) trapezoid |
_______________________ |
_________________ |
|
Space Shuttle compound |
_______________________ |
|
|
Boeing 747 trapezoid |
|
_________________ |
|
Concorde triangle |
|
_________________ |
HOME
EDUCATOR RESOURCES | AERONAUTIC EDUCATIONAL RESOURCES | INTERNET ACCESS RESEARCH | ICING RESEARCH TUNNEL
BEGINNER'S GUIDE TO AERONAUTICS | FREE SOFTWARE | AERODYNAMICS INFORMATION | AERODYNAMICS PROBLEMS | PROPULSION INFORMATION |
PROPULSION PROBLEMS | FOILSIM INFORMATION | FOILSIM PROBLEMS | ENGINESIM INFORMATION | ENGINESIM PROBLEMS | ROCKETMODELER
AERONAUTICS LESSONS & ACTIVITIES | WIND TUNNEL WEB PAGES | AERONAUTS 2000 | VIDEOCONFERENCES WITH THE U.K.
EDUCATOR RESOURCES | AERONAUTIC EDUCATIONAL RESOURCES | INTERNET ACCESS RESEARCH | ICING RESEARCH TUNNEL
BEGINNER'S GUIDE TO AERONAUTICS | FREE SOFTWARE | AERODYNAMICS INFORMATION | AERODYNAMICS PROBLEMS | PROPULSION INFORMATION |
PROPULSION PROBLEMS | FOILSIM INFORMATION | FOILSIM PROBLEMS | ENGINESIM INFORMATION | ENGINESIM PROBLEMS | ROCKETMODELER
AERONAUTICS LESSONS & ACTIVITIES | WIND TUNNEL WEB PAGES | AERONAUTS 2000 | VIDEOCONFERENCES WITH THE U.K.
Please send any comments to:
Curator: Tom.Benson@grc.nasa.gov
Responsible Official: Kathy.Zona@grc.nasa.gov
Curator: Tom.Benson@grc.nasa.gov
Responsible Official: Kathy.Zona@grc.nasa.gov