This slide shows the fin shapes for a variety of rockets as
viewed from the side while looking onto the fin. This view is called a
planform of the fin.
You can see that fins come in many different planforms:
rectangular, triangular, trapezoidal, or even elliptical.
To determine the aerodynamic force
that a fin generates, you must be able to calculate the area of any
of these shapes. This skill is taught in middle school and
used every day by design engineers.
The area is the two-dimensional amount of space that an object occupies.
Area is measured along the surface of an object and has dimensions of
length squared; for example, square feet of material, or centimeters squared.
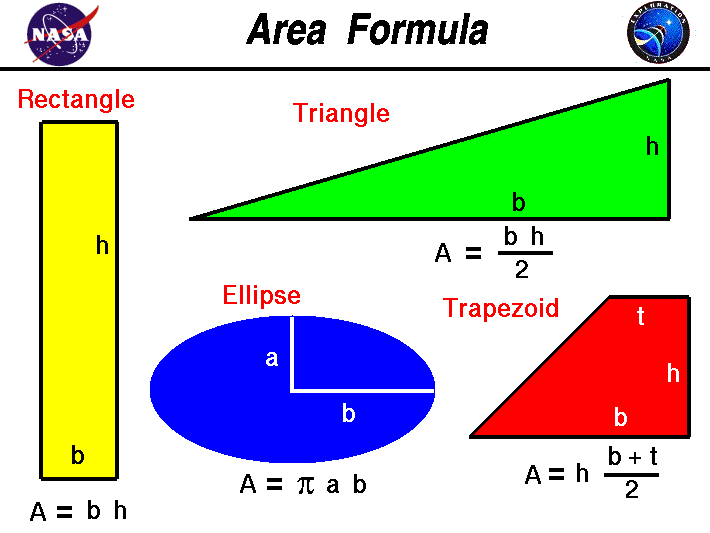
On the slide we have listed the formula to calculate
the area of a variety of shapes:
The area of a rectangle is equal to the
height h times the base b;
A = h * b
The equation for the area of a trapezoid
is one half the sum of the top t and bottom b times the height h;
A = h * [ t + b ] / 2
The area of a triangle is
equal to one half of the base b times the height h;
A = .5 * b * h
Some fins are
elliptically shaped. For an ellipse with a semi-axis a
and semi-axis b,
the area is given by:
A = pi * a * b
where pi is the ratio of the circumference to the diameter of a circle
and is equal to 3.1415. A special case of the ellipse is a circle, in
which the semi-axis is equal to the radius r. The area of a
circle is:
A = pi * r^2
If the root of an elliptical fin is given by cr and the distance
from the root to the tip is given by ct, the area of the fin is:
A = pi * cr *ct
For a compound configuration like the Space Shuttle, you have to break up the
fin into simple shapes which you can compute, and then add them together.
Guided Tours
-
 Rocket Aerodynamics:
Rocket Aerodynamics:

-
 Viscous Aerodynamics:
Viscous Aerodynamics:

-
 Scalars:
Scalars:

Activities:
Related Sites:
Rocket Index
Rocket Home
Beginner's Guide Home
|
