
|

|
+ Text Only Site
+ Non-Flash Version
+ Contact Glenn
|
|
|

|
How Jet Engines Work
Answers
|

|
- Use the Internet to find the function of the main parts of a
jet engine and complete the table of jet engine parts shown
below.
(See
http://www.grc.nasa.gov/WWW/K-12/airplane/turbparts.html
)
JET ENGINE PARTS
|
IMAGE OF PART
|
PART FUNCTION
|
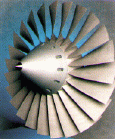
Fan
|
|
Accelerates air into the
jet engine.
Fans are used for efficiency.
|
By-pass Duct
|

|
Air flows through the
inlet through a duct and out the nozzle. The air leaves
the engine at a higher velocity than when it entered. The
passage through which the air travels is called the
by-pass duct.
|
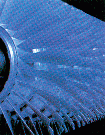
Compressor
|
|
Consists of multiple rows
of blades which turn and make the air
denser.
|
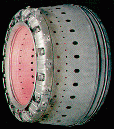
Combustor
|
|
The compressed air flows
into the combustor where a spray of fuel is added and
ignited.
|
Turbine
|

|
The fast moving air causes
the blades of the turbine to turn, generating energy
which is used to power other parts of the
engine.
|
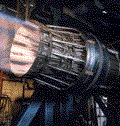
Nozzle
|
|
Air leaves the engine
through the nozzle where exhause pressure is matched with
atmospheric pressure.
|
- Name the four main types of gas
turbines (http://www.grc.nasa.gov/WWW/K-12/airplane/trbtyp.html)
demonstrated below and give their functions.
NAME OF ENGINE
|
DIAGRAM OF GAS TURBINE
|
MAIN APPLICATION OF
ENGINE
|
|
Turbojet
|
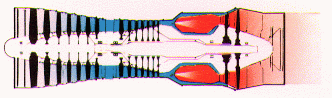
|
Airliners and military
aircraft
|
|
Turbo
fan
|
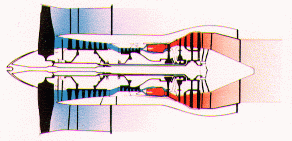
|
Most common
type used in civil and military
aircraft
|
|
Turbo prop
|
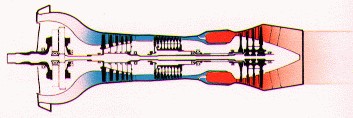
|
Military
aircraft
|
|
Turbo
shaft
|

|
Helicopters, power and
pumping stations, hovercraft, and
ships
|
Diagrams used in this table have the following
Copyright (C) 1995, 1996, 1997 Allison Engine Company. All rights
reserved
- The reaction produced by a jet engine is based on Newton's
Third law of motion.
- Explain Newton's law of motion referred to in Question 3.
For every action, there is an
equal and opposite reaction.
- Give two examples of applications of Newton's law of motion
other than jet engines.
Answers will vary.
Examples: a bouncing ball or one marble striking another
marble.
|
Related Pages:
Standards
Activity
Worksheet
Propulsion Activity Index
Propulsion Index
|
|
|
|
