

Drag Equation - Level 1
Answers
- Click on The
Drag Equation to open the appropriate slide. Study the equation
and read the explanation of this concept. Then use the information to
complete the questions below.
- In the following
table, identify each variable in the equation. State the appropriate
units for each value:
Variable Identity English Units Metric Units D Drag Newtons Pounds Cd Drag Coefficient No units No units r Density of air kg/m3 slug/ft3 V Velocity m/s ft\s A Reference Area m2 ft2
A. What possible reference areas (A) can be used to compute the drag?
Total surface area of aircraft, frontal area of aircraft, or wing area.
B. If we want to compute the L/D (lift to drag ratio), which reference area would we want to use? Why?
Wing area, since lift is computed using the wing area.
C. Besides reference area, air density, and velocity, drag depends on several other values. What variable is used to model many of the complex dependencies of drag? What are some of the dependencies of drag incorporated in this value?
Cd - drag coefficient. Some of the dependencies of drag incorporated in this value are shape, inclination and some flow conditions. - Calculate the following
problems which involve the drag of an aircraft: (Before computing,
make sure all units agree)
A. Suppose you are flying an aircraft with the following wing shape and dimensions. What is the total wing area?
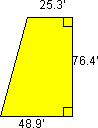
A = 1/2h(b1 + b2) = 1/2 x 76.48(25.3 + 48.9) = 2834.44 ft2 for one wing
= 5668.88 ft2 for both wings
B. The thrust of the aircraft is 120,000 pounds and the air density is .00048 slugs/cu.ft. The current cruising speed is 450 mph and we need to determine the drag coefficient of the aircraft. Find the Cd. (Hint: you may want to convert the original equation first)Cd = 2D/(r x V2 x A) = 2(120,000)/(.00048)(450)2(5668.88) = .436
C. Weather conditions force the aircraft to descend to a level where the air density is .00076 slugs/cu.ft. The engine thrust increases to 250,000 pounds. At the new cruising altitude, what is the speed of the aircraft? (Hint: once again, you may want to convert the equation first)
V =sqrt(2D/Cd x r x A)=sqrt(2x(250,000)/(.436 x .00076 x 5668.88)) = 516 mph
EDUCATOR RESOURCES | AERONAUTIC EDUCATIONAL RESOURCES | INTERNET ACCESS RESEARCH | ICING RESEARCH TUNNEL
BEGINNER'S GUIDE TO AERONAUTICS | FREE SOFTWARE | AERODYNAMICS INFORMATION | AERODYNAMICS PROBLEMS | PROPULSION INFORMATION |
PROPULSION PROBLEMS | FOILSIM INFORMATION | FOILSIM PROBLEMS | ENGINESIM INFORMATION | ENGINESIM PROBLEMS | ROCKETMODELER
AERONAUTICS LESSONS & ACTIVITIES | WIND TUNNEL WEB PAGES | AERONAUTS 2000 | VIDEOCONFERENCES WITH THE U.K.
Curator: Tom.Benson@grc.nasa.gov
Responsible Official: Kathy.Zona@grc.nasa.gov