

Answers
- What is the smallest
angle in degrees between the lift and drag forces?
(a) 0o (b) 90o (c) 180o (d) 270o (e) 360o
- What is the smallest
angle in degrees between the weight and lift forces?
(a) 0o (b) 90o (c) 180o (d) 270o (e) 360o
- What is the smallest
angle in degrees between the thrust and drag forces?
(a) 0o (b) 90o (c) 180o (d) 270o (e) 360o
- What is the smallest
angle in degrees between the weight and thrust forces?
(a) 0o (b) 90o (c) 180o (d) 270o (e) 360o
- When an airplane
(or any object) is moving at a constant speed, the forces acting on
the airplane must be
(a) unbalanced, which means that the total force is not zero.
(b) balanced, which means that the total force is zero.
A fighter jet is flying at 37,000 feet with a constant speed of 1,310 km/h. The jet has a weight of 110,000 N and its engines provide a thrust of 106,752 N (using afterburners).
- What is the jet's
height (altitude) in meters?
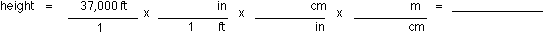
Step 1: Recall that 12 inches = 1 foot, 2.54 cm = 1 inch, and 100 cm = 1 meter.
Step 2: Write these unit factors in their appropriate places in the factor multiplication.
(a) 1.13 x 108 m (b) 61,248 m (c) 8,679 m (d) 356 m (e) 11,277.6 m - What is the jet's
mass? [Hint: Use F = mag = W, where ag
= 9.8 m/s2.]
Step 1: force = weight = 110,000 N; a = 9.8 m/s2 (acceleration due to gravity)Step 2: mass = force / acceleration
(a) 520,120 kg (b) 11,224.49 kg (c) 3,527 kg (d) 614,853 kg (e) 215 kg - How much lift force
is being applied to the jet?
Realize that if the airplane's speed is constant, the forces acting on the airplane must be balanced.Force of lift = Force of weight
(a) 512,128 N (b) 5,634 N (c) 110,000 N (d) 9,935 N (e) 106,752 N
- If the jet engines
are creating a thrust of 106,752 N, what is the drag force applied to
the jet?
Realize that if the airplane's speed is constant, the forces acting on the airplane must be balanced.Force of drag = Force of thrust
(a) 512,128 N (b) 5,634 N (c) 110,000 N (d) 9,935 N (e) 106,752 NSuppose the jet engines are providing a thrust of 100,102 N while the drag force is only 90,167 N.
- What is the total
unbalanced (or net) force on the jet?
Step 1: Fthrust = 100,102 N; Fdrag = 90,167 NStep 2: Ftotal = Fthrust - Fdrag ( Fnet = Ftotal)
(a) 512,128 N (b) 5,634 N (c) 110,000 N (d) 9,935 N (e) 106,752 N - What will be the
jet's acceleration?
Step 1: F = 9,935 N; m = 11,224.49 kgStep 2: acceleration = force / mass
(a) 0.89 m/s2 (b) 4.35 m/s2 (c) 0.36 m/s2 (d) 4,253 m/s2 (e) 65.3 m/s2 - If the jet is cruising
at 223.47 m/s and accelerates at 0.25 m/s2 for 1,530 seconds,
what is the jet's final speed?
Step 1: vi = initial velocity = 223.47 m/s; a = 0.25 m/s2; t = 1,530 sec (vf = final velocity)
Step 2: a = ( vf - vi ) / t
a) 401.28 m/s (b) 605.97 m/s (c) 731.67 m/s (d) 634,521.6 m/s (e) 3,452 m/s - Using the data
from the previous problem, calculate how far the jet traveled while
it accelerated during the 1,530 seconds.
Step 1: vi = 223.47 m/s; a = 0.25 m/s2; t = 1,530 sec; di = initial distance = 0 m (df = final distance)Step 2: df = ( 1 / 2 ) at2 + vit + di
(a) 401.28 m (b) 605.97 m (c) 731.67 m (d) 634,521.6 m (e) 3,452 m - If the jet cruised
at a speed of 1,310 km/h for 2.53 hours, how far did it travel?
Step 1: v = 1310 km/hr.; t = 2.53 hr.Step 2: d = vt
(a) 517.79 km (b) 4,639.00 km (c) 218.42 km (d) 6,547.23 km (e) 3,314.30 km
EDUCATOR RESOURCES | AERONAUTIC EDUCATIONAL RESOURCES | INTERNET ACCESS RESEARCH | ICING RESEARCH TUNNEL
BEGINNER'S GUIDE TO AERONAUTICS | FREE SOFTWARE | AERODYNAMICS INFORMATION | AERODYNAMICS PROBLEMS | PROPULSION INFORMATION |
PROPULSION PROBLEMS | FOILSIM INFORMATION | FOILSIM PROBLEMS | ENGINESIM INFORMATION | ENGINESIM PROBLEMS | ROCKETMODELER
AERONAUTICS LESSONS & ACTIVITIES | WIND TUNNEL WEB PAGES | AERONAUTS 2000 | VIDEOCONFERENCES WITH THE U.K.
Curator: Tom.Benson@grc.nasa.gov
Responsible Official: Kathy.Zona@grc.nasa.gov