

Geometry
Problem Set II
If so instructed by your teacher, print out a worksheet page for these problems.
If so instructed by your teacher, print out a worksheet page for these problems.
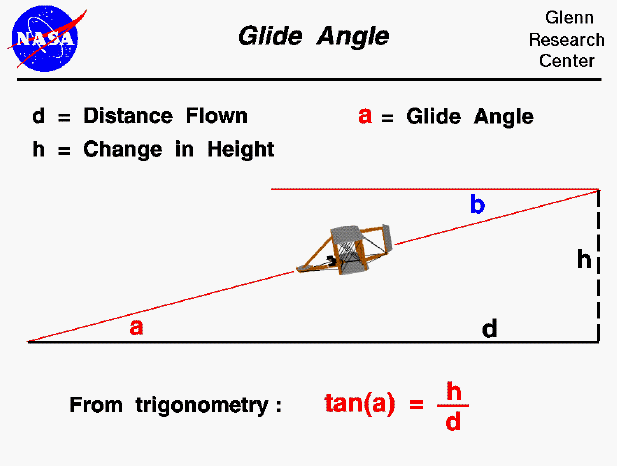
Open the slide called Glide Angle (with text) to learn about how a glide angle measures the flying efficiency of the glider
If a glider is in a steady (constant velocity and no acceleration) descent, it loses altitude as it travels across the ground. The glider's flight path will be a simple straight line, shown as the inclined red line in the figure. The flight path will intersect the ground at an angle "a" called the glide angle. The top line in the figure represents the horizontal path of the plane before its descent and is parallel to the ground.
Problem:
Prove angle a is congruent to angle b, given the above relationships.
HOME
EDUCATOR RESOURCES | AERONAUTIC EDUCATIONAL RESOURCES | INTERNET ACCESS RESEARCH | ICING RESEARCH TUNNEL
BEGINNER'S GUIDE TO AERONAUTICS | FREE SOFTWARE | AERODYNAMICS INFORMATION | AERODYNAMICS PROBLEMS | PROPULSION INFORMATION |
PROPULSION PROBLEMS | FOILSIM INFORMATION | FOILSIM PROBLEMS | ENGINESIM INFORMATION | ENGINESIM PROBLEMS | ROCKETMODELER
AERONAUTICS LESSONS & ACTIVITIES | WIND TUNNEL WEB PAGES | AERONAUTS 2000 | VIDEOCONFERENCES WITH THE U.K.
EDUCATOR RESOURCES | AERONAUTIC EDUCATIONAL RESOURCES | INTERNET ACCESS RESEARCH | ICING RESEARCH TUNNEL
BEGINNER'S GUIDE TO AERONAUTICS | FREE SOFTWARE | AERODYNAMICS INFORMATION | AERODYNAMICS PROBLEMS | PROPULSION INFORMATION |
PROPULSION PROBLEMS | FOILSIM INFORMATION | FOILSIM PROBLEMS | ENGINESIM INFORMATION | ENGINESIM PROBLEMS | ROCKETMODELER
AERONAUTICS LESSONS & ACTIVITIES | WIND TUNNEL WEB PAGES | AERONAUTS 2000 | VIDEOCONFERENCES WITH THE U.K.
Please send any comments to:
Curator: Tom.Benson@grc.nasa.gov
Responsible Official: Kathy.Zona@grc.nasa.gov
Curator: Tom.Benson@grc.nasa.gov
Responsible Official: Kathy.Zona@grc.nasa.gov